By Rushda Niyas and Deenah Mahroof
As a business owner, it’s important to understand the importance of data privacy for your company. With the increasing use of technology and the collection of personal data, protecting sensitive information has become more crucial than ever. In this blog post, we’ll be discussing the basics of data privacy and why it should be a top priority for your business. We’ll also delve into the concept of personal data, including what it is and the legal requirement to protect it. By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of the importance of data privacy and how it applies to your business.
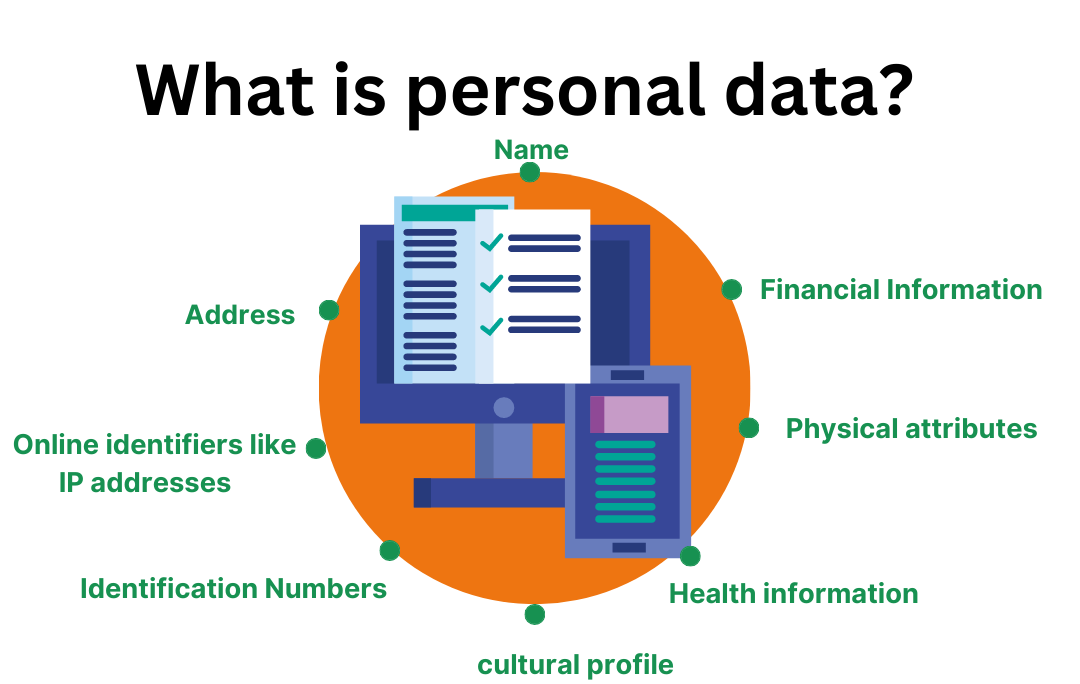
Why protect personal data?
Data protection refers to a set of measures aimed at safeguarding sensitive and personal information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or destruction. This is crucial for maintaining privacy and security for individuals and institutions, by ensuring the confidentiality, accuracy, and availability of data, while preventing security breaches and other malicious activities.
Effective data protection strategies involve implementing policies, procedures, and technologies to safeguard data throughout its lifecycle, from collection and storage to processing and sharing.
Are you legally obliged to protect the data you deal with?
If your business collects personal data from customers in different jurisdictions, it may be subject to different data protection laws. It’s important to understand and comply with all applicable laws to minimize potential liabilities. Therefore, it’s crucial to be aware of your obligations under each relevant law to ensure that you’re protecting your customers’ data appropriately and avoiding any legal consequences. Let’s look at two data protection laws which would be applicable to you, if you have customers in Sri Lanka or the EU.
Complying with data protection laws offers numerous advantages. Not only is it a legal requirement, but it also makes economic sense as it can save time and money. Additionally, it demonstrates that an organization values individuals’ information, which can enhance its reputation and brand image. Adhering to data protection laws not only meets legal obligations but can also bring economic benefits and contribute to a positive public perception of an organization.
The Sri Lankan Law
Sri Lanka’s “Personal Data Protection Act of 2022” (PDPA), was enacted in March 2022. The PDPA was modelled, relying heavily on the “General Data Protection Regulations” (GDPR) of the European Union (EU). The Act regulates all aspects of data protection, such as the rights of data subjects (those whose data is being collected) while simultaneously facilitating the growth and innovation of the digital economy in Sri Lanka; the duties of data processors/controllers and the consequences for non-compliance with the PDPA.
The Act is heavily influenced by GDPR principles such as legitimate purpose, proportionality, transparency, accuracy, limited retention, integrity, and accountability. The Act also intends to enhance collaboration across borders while ensuring that personal data protection frameworks are interoperable.
The PDPA is intended to be applicable to both local and foreign entities, including those providing goods or services to Sri Lankans, and particularly focuses on individuals’ data in Sri Lanka. This could also include digital platforms offering services to Sri Lankans from locations outside of Sri Lanka. However, the PDPA is yet to come into force and will be effective when gazetted between 19th September, 2023 and 19th March 2025.
GDPR
The GDPR is a EU law which was enacted in May 2018 and applies to all businesses operating within the EU, as well as those that offer goods or services to EU residents or monitor their behavior. Its main purpose is to protect the fundamental rights of individuals whose personal and sensitive data is held by organizations. The GDPR grants EU residents more control over how their personal data is used by organizations and gives them the right to access and delete their personal information. The GDPR empowers EU residents by providing them with greater authority over their personal data.
GDPR applies to all persons or entities handling personal data within the EU. Countries outside the EU handling personal data are referred to as “Third Countries” under GDPR. Although they may have their own data protection laws, they are obligated to adhere to the GDPR, when supplying goods or services to the EU or when processing data concerning individuals who live within the EU.
Is GDPR relevant to you as a Sri Lankan entity?
If you interact with EU businesses or collect personal data of EU citizens, then the GDPR applies to you, and you must ensure compliance with the regulation, in order to prevent the loss of conducting such businesses.
Usually, the GDPR is not directly enforced on individuals of third countries, instead EU authorities enforce regulations on EU entities which engage with such individuals. As a result, EU entities may terminate connections with GDPR non-compliant third country entities, and you may face the risk of business termination if you do not comply with the GDPR.
Companies engaged in significant EU personal data processing are required to implement suitable measures, as described above, to fulfill the prerequisites for transferring EU personal data to third countries.
What are the consequences to your business for not taking data protection seriously?
Two of the significant consequences your business may face due to non-compliance are (1) “legal consequences” such as fines and penalties, regulatory scrutiny, lawsuits; and (2) “business consequences”, such as business disruption, and reputational/brand damage.
The Largest recorded Fines for non-compliance with GDPR.
Noncompliance with GDPR can result in significant consequences, including high fines. In the past four years, some companies have faced fines in the nine-digit range for failing to comply with GDPR. This has affected not only big tech companies such as Google, Amazon, Meta but also any business that conducts online operations. Data protection supervisory authorities across Europe have issued fines totaling €1.64bn since January 28th, 2022, and a total of €2.34bn has been issued in GDPR fines so far. There has been a year-on-year increase in aggregate reported GDPR fines of 50%, with ad-tech and behavioral advertising being a top enforcement priority in 2022.

ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DATA PRIVACY
The rapidly evolving generative Artificial Intelligence technology will give rise to substantial privacy concerns. Regulations will be forthcoming, with the European Union expected to introduce new regulations on AI later this year.
Language Models like OpenAI’s GPT, use large amounts of data to learn patterns and make predictions. This data can come from a variety of sources, including publicly available texts and private data sets. In order to train, LLMs typically require access to large amounts of diverse text data, which may include personal information such as names, email addresses, and other identifying details.
Companies developing AI tech must have clear policies and procedures in place to ensure that personal data is collected and used in compliance with applicable data protection laws. This may include obtaining user consent, implementing data protection measures, and allowing users to exercise their rights under GDPR.
Some data privacy concerns due to the rapid adoption of AI technology:
Lack of transparency: AI algorithms are often opaque, making it difficult to understand how they make decisions. This lack of transparency can prevent individuals from understanding how their personal data is being used.
Inadequate consent: Obtaining informed consent from individuals is a key component of data privacy. However, AI algorithms may use data in ways that individuals did not anticipate or could not have foreseen, leading to inadequate consent.
Data breaches: As AI systems store and process large amounts of personal data, they may become targets for hackers or suffer from other vulnerabilities, leading to data breaches and violations of data privacy.
Repurposing of data: AI systems may repurpose data collected for one purpose for use in another context, without individuals’ consent or knowledge. This can raise significant privacy concerns.
Privacy risks in autonomous decision-making: AI systems increasingly make autonomous decisions, such as in self-driving cars or automated loan approvals. This creates privacy risks, as sensitive personal data is used to make decisions without individuals having a say in the outcome.
Some steps AI companies can adopt to be compliant:
Data Minimization: Companies should only collect and process the minimum amount of personal data necessary to achieve the specific purpose for which it was collected. In the context of AI development, companies should ensure that they are not collecting or processing personal data that is not relevant or necessary for the training of their AI models.
User Consent: Companies must obtain explicit and informed consent from users before collecting, processing or sharing their personal data. Companies must also clearly state the purpose for which the data will be used and obtain separate consent for each purpose. This is particularly important in the context of AI development, as users should be aware of how their data is being used to train the AI models.
Transparency: Companies must be transparent about how they collect, process and use personal data. In the context of AI development, companies should provide clear and easily understandable information about the AI models they are developing and how they use personal data to train them.
Data Security: Companies must take appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security and integrity of personal data. This is particularly important in the context of AI development, as the data used to train AI models is often sensitive and confidential.
Right to Access and Erasure: Companies must allow users to access and erase their personal data upon request. In the context of AI development, companies should ensure that users can easily access and delete their data that has been used to train AI models.
Are you a Sri Lankan entity and think you might be dealing with personal data of your customers?
What can you do to ensure you are compliant?
Consider the following questions and conduct a self-assessment
- Are you in an industry that collects personal data of your customers? For example,
- Banking and Securities
- Media and Entertainment
- Pharma and Healthcare
- Education
- Insurance
- Energy and Utilities
- Transportation
- Who are your customers? Identify the jurisdiction of your customers.
- What is your data protection policy presently? Do an internal audit of your data collection, processing, and retention policies.
- Do you need to take any steps to ensure that you are compliant with the data protection laws that may apply to you?


